#include <DomText.h>
Inherits xmldom::DomCharacterData.
Inherited by xmldom::DomCDATASection.
Inheritance diagram for xmldom::DomText:

DomText interface inherits from DomCharacterData and represents the textual content (termed character data in XML) of an DomElement or DomAttribute.
If there is no markup inside an element's content, the text is contained in a single object implementing the DomText interface that is the only child of the element. If there is markup, it is parsed into the information items (elements, comments, etc.) and DomText nodes that form the list of children of the element.
When a document is first made available via the DOM, there is only one DomText node for each block of text. Users may create adjacent DomText nodes that represent the contents of a given element without any intervening markup, but should be aware that there is no way to represent the separations between these nodes in XML or HTML, so they will not (in general) persist between DOM editing sessions.
The normalize() method on DomNode merges any such adjacent DomText objects into a single node for each block of text.
Public Member Functions | |
| DomText () | |
| ctor | |
| DomText (const DomText ©) | |
| copy ctor | |
| virtual | ~DomText () |
| dtor | |
| const DomText & | operator= (const DomText &assign) |
| assign | |
DOM Level 1 | |
| DomText | splitText (XmlSize offset) |
Breaks this node into two nodes at the specified offset, keeping both in the tree as siblings. | |
DOM Level 3 | |
| bool | isWhitespaceInElementContent () const |
| Returns whether this text node contains element content whitespace, often abusively called "ignorable whitespace". | |
| DomString | getWholeText () |
| Returns all text of Text nodes logically-adjacent text nodes to this node, concatenated in document order. | |
| DomText | replaceWholeText (const DomString &content) |
| Replaces the text of the current node and all logically-adjacent text nodes with the specified text. | |
Non-standard extension | |
| bool | isIgnorableWhitespace () const |
| Return true if this node contains ignorable whitespaces only. | |
| xmldom::DomText::DomText | ( | ) |
ctor
| xmldom::DomText::DomText | ( | const DomText & | copy | ) |
copy ctor
| xmldom::DomText::~DomText | ( | ) | [virtual] |
dtor
| DomText xmldom::DomText::splitText | ( | XmlSize | offset | ) |
Breaks this node into two nodes at the specified offset, keeping both in the tree as siblings.
After being split, this node will contain all the content up to the offset point. A new node of the same type, which contains all the content at and after the offset point, is returned. If the original node had a parent node, the new node is inserted as the next sibling of the original node. When the offset is equal to the length of this node, the new node has no data.
| offset | The 16-bit unit offset at which to split, starting from 0. |
| bool xmldom::DomText::isWhitespaceInElementContent | ( | ) | const |
Returns whether this text node contains element content whitespace, often abusively called "ignorable whitespace".
The text node is determined to contain whitespace in element content during the load of the document or if validation occurs while using DomDocument.normalizeDocument().
| DomString xmldom::DomText::getWholeText | ( | ) |
Returns all text of Text nodes logically-adjacent text nodes to this node, concatenated in document order.
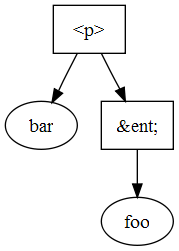
For instance, in the example below wholeText on the Text node that contains "bar" returns "barfoo", while on the Text node that contains "foo" it returns "barfoo".
Replaces the text of the current node and all logically-adjacent text nodes with the specified text.
All logically-adjacent text nodes are removed including the current node unless it was the recipient of the replacement text. This method returns the node which received the replacement text. The returned node is:
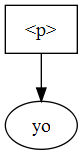
DomText or DomCDATASection) as the current node inserted at the location of the replacement.For instance, in the above example calling replaceWholeText on the Text node that contains "bar" with "yo" in argument results in the following:
Where the nodes to be removed are read-only descendants of an DomEntityReference, the DomEntityReference must be removed instead of the read-only nodes. If any DomEntityReference to be removed has descendants that are not DomEntityReference, DomText, or DomCDATASection nodes, the replaceWholeText() method must fail before performing any modification of the document, raising a DomException with the code NoModificationAllowedErr.
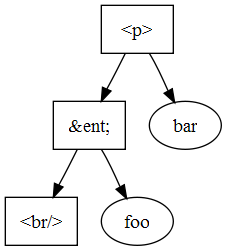
For instance, in the example below calling replaceWholeText() on the DomText node that contains "bar" fails, because the DomEntityReference node "ent" contains an DomElement node which cannot be removed.
| content | The content of the replacing DOMText node. |
| bool xmldom::DomText::isIgnorableWhitespace | ( | ) | const |
Return true if this node contains ignorable whitespaces only.
 1.5.2
1.5.2